The nerve sheath includes the Schwann cells, which surround individual axis cylinders; perineural fibroblasts, which form collagen networks between individual nerve fibers with their surrounding Schwann cells; and the epineurium, a sheath that envelops entire nerve trunks and that is composed of fibroblastic-type cells and collagen.
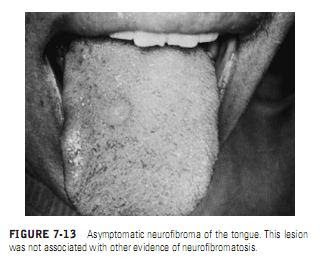
Most nerve sheath tumors are true neoplasms. The developmental abnormalities (ie, hamartomas and not neoplasms) of neurofibromatosis and traumatic neuroma arise from nerve sheath cells. Neurofibromas of the oral cavity are usually solitary;a significant feature of neurofibroma is its tendency to be multiple and to be associated with a variety of other familial abnormalities in the syndrome of von Recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis, an inherited autosomal dominant condition in which there is also a tendency to develop sarcoma (see the later section, “Syndromes with Benign Oral Neoplastic or Hamartomatous Components”). Neurofibromatosis evolves as a consequence of a mutation in the NF1 gene. Since 5% of patients with neurofibromatosis develop sarcoma,recognition of an otherwise innocentappearing nodule in the oral cavity as a neurofibroma can be an important diagnosis.Histologically, neurofibromas are to be distinguished from neurilemomas (tumors of the nerve sheath, or schwannomas). Neurilemomas are encapsulated S-100 protein–positive tumors that show patterns of whorled connective-tissue elements interspersed with readily recognizable axons with or without a myelin sheath. Neurilemomas also exhibit a characteristic palisading of nuclei and other suggestions of a histologic organization referred to as an organoid structure; both features are usually absent from neurofibromas and neuromas.Rarely, neurilemomas may occur in patients with neurofibromatosis. Oral lesions are usually asymptomatic and do not recur after local excision (Figure 7-13).
The term “traumatic neuroma” describes a localized exuberant growth of nerve and nerve sheath elements that develop after section or other local damage to a peripheral nerve.