The patient usually presents to the clinician with full-blown oral and systemic disease, but a history of the mode of onset is helpful in differentiating lesions of primary HSV infection from other acute multiple lesions of the oral mucosa. The incubation period is most commonly 5 to 7 days but may range from 2 to 12 days.
Patients with primary oral herpes have a history of generalized prodromal symptoms that precede the local lesions by 1 or 2 days. This information is helpful in differentiating this viral infection from allergic stomatitis or erythema multiforme, in which local lesions and systemic symptoms appear together. These generalized symptoms include fever, headache, malaise, nausea, and vomiting. A negative past history of recurrent herpes labialis and a positive history of direct intimate contact with a patient with primary or recurrent herpes are also helpful in making the diagnosis.
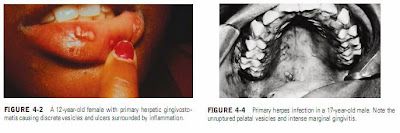
Approximately 1 or 2 days after the prodromal symptoms occur, small vesicles appear on the oral mucosa; these are thin-walled vesicles surrounded by an inflammatory base (Figure 4-2). The vesicles quickly rupture, leaving shallow round discrete ulcers. The lesions occur on all portions of the mucosa. As the disease progresses, several lesions may coalesce, forming larger irregular lesions.
An important diagnostic criterion in this disease is the appearance of generalized acute marginal gingivitis. The entire gingiva is edematous and inflamed (Figures 4-3, A and B, and 4-4). Several small gingival ulcers are often present. Examination of the posterior pharynx reveals inflammation, and the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes are characteristically enlarged and tender. On occasion, primary HSV may cause lesions of the labial and facial skin without intraoral lesions.
Primary HSV in otherwise healthy children is a self-limiting disease. The fever ordinarily disappears within 3 or 4 days, and the lesions begin healing in a week to 10 days, although HSV may continue to be present in the saliva for up to a month after the onset of disease.